This application uses GitHub API accesed through REST.
Quick start
Download GitSearch.jar and run it.
JSON, REST, and GitHub API
JSON
JavaScript Object Notation or JSON is a lightweight data-interchange format easily readable/writable by both humans and computers. JSON is language-independent, but uses conventions reminiscent of the C-family language (C, C++, C#, Java, JavaScript, Perl, Python, etc.). These properties make JSON an ideal data-interchange language.
JSON is composed of these two structures:
- A collection of name/value pairs. This is realized in various programming languages as an object, record, struct, dictionary, hash table, keyed list, or associative array.
- An ordered list of values. This is realized as an array, vector, list, or sequence.
In JSON, they take on these forms:
- An object is an unordered set of name/value pairs. An object begins with
{(left brace) and ends with}(right brace). Each name is followed by:(colon) and the name/value pairs are separated by,(comma). - An array is an ordered collection of values. An array begins with
[(left bracket) and ends with](right bracket). Values are separated by,(comma). - A value can be a string in double quotes, a number, logical values (true/false), null, or other objects/arrays. JSON allows nested structures.
- A string is a sequence of Unicode characters wrapped in
"(double quotes) with backslash escapes. A character is a single-character string. - A number is like a C or Java number, except that octal and hexadecimal numbers cannot be used.
- A string is a sequence of Unicode characters wrapped in
- Whitespace can be inserted between any pairs of tokens.
REST
Representational State Transfer or REST is a communication architecture standard which most commonly uses HTTP to exchange data. With REST, a REST server provides access to resources (data) to be accessed by a REST client. Each resource is identified by a Uniform Resource Identifier (URI) and is represented as plaintext, JSON, or XML. A REST client sends resource request using HTTP methods:
- GET – read-only access to a resource
- PUT – create new resource
- DELETE – remove a resource
- POST – update an existing resource or create new resource
- OPTIONS – get supported operations on a resource
Web services which uses REST as an underlying architecture is called RESTful web services. On a RESTful web service, a client sends a HTTP request and expects a HTTP response from a server. An HTTP request is composed of the methods used to create said request, current HTTP verrsion, metadata for the request (request header), and contents of the request (request body). An HTTP response is composed of the server status (response code), current HTTP version, metadata for the response (response header), and the data itself (response body).
The client/server communication is constrained by no client context being stored on the server between requests. This constraint is defined as statelessness. With this, web services can serve each request independently and do not need to maintain client state, which simplifies the application and increases performance.
GitHub API
The GitHub API is an application programming interface (API) provided by GitHub to access its resources. All GitHub API access is over HTTPS using REST and accessed from https://api.github.com. All data is sent and received as JSON.
A request for individual resources will elicit a detailed response typically containing all attributes for that resource. Meanwhile, a request for a list of resources will elicit a summary response containing a subset of attributes for that resource for performance reasons.
This application specifically uses the GitHub Search API. This particular API is used to perform specific searches on resources based on a search query (user, files on repositories, etc.) and returns a list of items based on the input query. Each query produces a maximum of 1000 results, sorted on relevance by default unless specified otherwise. Requests are limited to 30 authenticated requests and 10 unauthenticated requests per minute.
Application Features
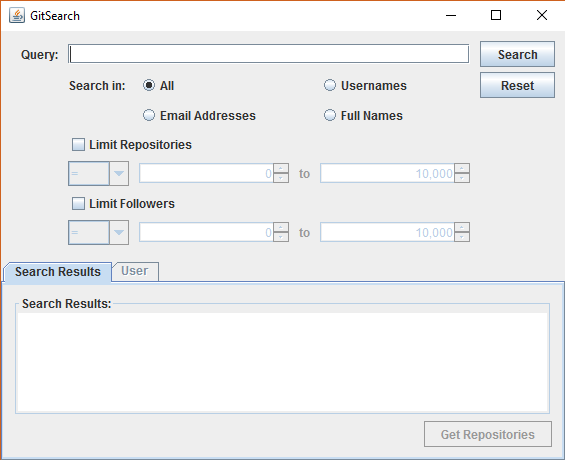
GitSearch allows searching for users based on their usernames, email addresses, full names, or all of them. Searching can be filtered through their number of repositories or followers.
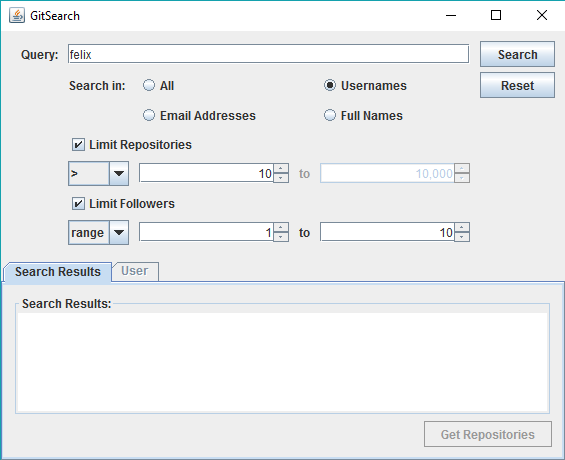
Repositories and followers can be filtered with an exact number (the = operator), a comparison operator (the >, >=, <, and <= operators), or within a range of numbers (inclusive).
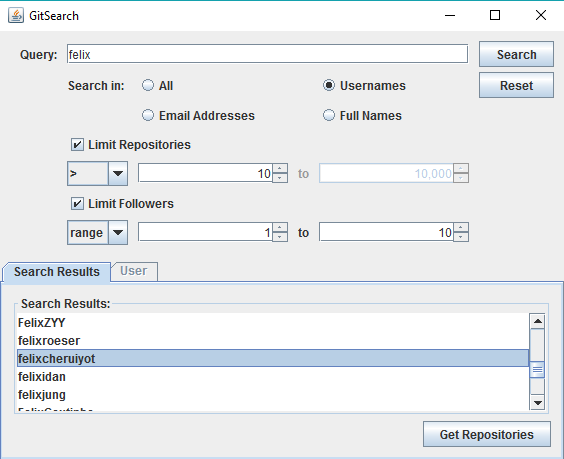
Search results will be displayed in the list in the lower panel. Select a username to retrieve their repositories.

Repositories will be displayed in a different tab in the lower panel. In case the cell is not large enough to fully display the contents of the cell, hovering over it will display a tooltip which contains the full contents of the cell. Double-clicking the repository URL will open the URL in your desktop browser.
The search results will still be available in the first tab. Selecting a different username, then retrieving their repositories will overwrite the repositories of the currently retrieved user. Similiarly, searching for a new query will overwrite the current search results, though the retrieved repositories will persist until another user has their repositories retrieved.